Introduction
In today’s digital world, information is one of the most valuable assets for individuals and organizations alike. From personal emails and banking details to business data and intellectual property, safeguarding information has never been more critical. This is where information security comes into play. Information security, also known as InfoSec, focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, theft, loss, or damage. It ensures that sensitive information remains confidential, accurate, and accessible only to authorized users.
Whether you are a student, a professional, or a business owner, understanding the basics of information security is essential. With cyberattacks and data breaches increasing every year, a single security lapse can lead to serious financial and reputational consequences. Organizations spend millions on information security measures, and even individuals must take steps to protect their personal data.
This article will provide a complete guide to information security, explaining what it is, why it is important, how to implement it effectively, and the benefits and risks associated with it. We will also cover common mistakes to avoid, expert tips, and frequently asked questions to give you a well-rounded understanding of this crucial topic. By the end, you will have a clear roadmap for protecting your data in both personal and professional contexts.
What is Information Security?
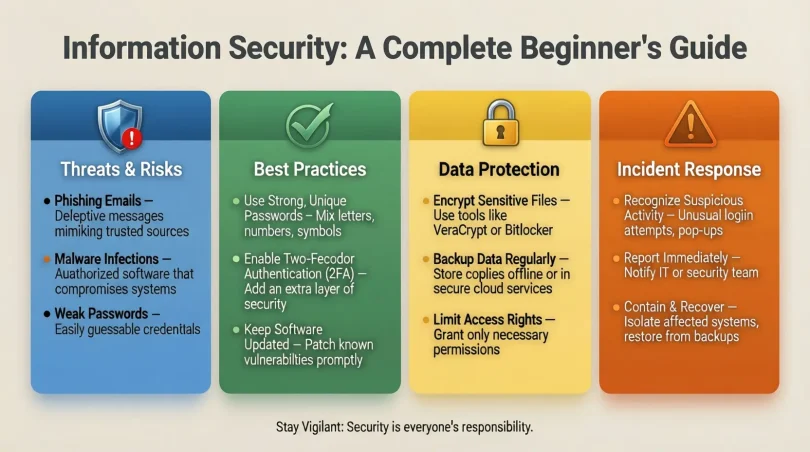
Information security is the practice of protecting information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It is a broad discipline that includes both digital and physical data protection measures. At its core, information security focuses on three key principles, often referred to as the CIA Triad:
- Confidentiality – Ensuring that information is accessible only to those who have the proper authorization.
- Integrity – Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of data, preventing unauthorized alterations.
- Availability – Making sure that information is accessible to authorized users when needed.
Information security is not just about installing antivirus software or firewalls; it is a combination of technologies, policies, and best practices designed to safeguard sensitive data. This can include password management, encryption, access controls, and employee training.
It is important to note that information security applies to all types of information, including digital files, printed documents, and even verbal communication. In an era where remote work and cloud storage are common, the boundaries between physical and digital security are increasingly blurred.
Why is Information Security Important?
The importance of information security cannot be overstated. Data breaches, cyberattacks, and identity theft are becoming more frequent, and the consequences can be severe. Here are some key reasons why information security matters:
- Protects Sensitive Data: Personal, financial, and business data must be protected to prevent unauthorized access.
- Prevents Financial Loss: Cyberattacks can lead to significant monetary loss due to fraud or data theft.
- Maintains Reputation: Organizations that fail to protect data can suffer reputational damage.
- Ensures Compliance: Many industries have regulations that require strict information security measures.
- Supports Business Continuity: Proper information security measures ensure that operations continue smoothly during security incidents.
For example, consider a company that stores customer credit card information. If a cybercriminal accesses this data, the company can face legal consequences, loss of customer trust, and financial penalties. On a personal level, failing to secure your online accounts can lead to identity theft or unauthorized transactions.
In short, information security is essential for protecting data, maintaining trust, and ensuring long-term success in both personal and professional contexts.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Information Security
Implementing information security may seem complex, but breaking it into practical steps makes it manageable. Here’s a step-by-step guide for beginners and intermediate users:
Step 1: Identify Your Data and Assets
- List all sensitive information you possess, such as personal records, business documents, or customer data.
- Identify devices and systems where data is stored, including computers, servers, and cloud storage.
- Categorize data based on sensitivity – critical, confidential, or public.
Step 2: Assess Risks
- Evaluate potential threats such as hacking, phishing, malware, or natural disasters.
- Consider the likelihood and potential impact of each threat.
- Prioritize risks to focus on the most significant vulnerabilities first.
Step 3: Implement Security Measures
- Passwords and Authentication: Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive files and communications to prevent unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and Antivirus: Install firewalls and antivirus software to detect and block threats.
- Access Controls: Limit access to sensitive data based on roles and responsibilities.
Step 4: Backup Data Regularly
- Create regular backups of important files.
- Use multiple storage methods, such as external drives and cloud storage.
- Test backups periodically to ensure they can be restored successfully.
Step 5: Educate Users
- Train employees or household members on security best practices.
- Teach them to recognize phishing attempts and suspicious links.
- Encourage a culture of security awareness.
Step 6: Monitor and Update
- Regularly monitor systems for unusual activity.
- Update software and systems to patch vulnerabilities.
- Review and update security policies as new threats emerge.
Step 7: Respond to Incidents
- Have a clear plan for responding to security breaches.
- Quickly isolate affected systems to prevent further damage.
- Notify relevant stakeholders and take corrective actions.
Benefits of Information Security

Implementing proper information security measures offers several benefits:
- Protects Confidential Information: Ensures sensitive data is safe from unauthorized access.
- Prevents Cybercrime: Reduces the risk of hacking, phishing, and malware attacks.
- Maintains Business Reputation: Companies with strong security gain customer trust.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Meets legal and industry-specific requirements.
- Supports Business Continuity: Minimizes downtime during security incidents.
- Improves Operational Efficiency: Secure systems are more reliable and stable.
Disadvantages / Risks of Poor Information Security
Failing to implement effective information security measures can result in:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Financial Loss: Theft, fraud, and recovery costs can be expensive.
- Reputational Damage: Loss of trust among customers, partners, and employees.
- Legal Consequences: Non-compliance with regulations can lead to penalties.
- Operational Disruption: Malware or attacks can halt business operations.
- Identity Theft: Personal information can be used for fraudulent purposes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Information Security
Even with security measures in place, mistakes can weaken protection. Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Weak Passwords: Using simple or repeated passwords makes accounts vulnerable.
- Ignoring Updates: Failing to update software can leave systems exposed.
- Neglecting Backups: Not backing up data increases risk of permanent loss.
- Overlooking Employee Training: Human error is a major cause of breaches.
- Poor Access Controls: Giving unnecessary access to sensitive data can lead to leaks.
- Assuming Security is One-Time: Information security is ongoing, not a one-off task.
FAQs About Information Security
1. What is the difference between information security and cybersecurity?
Information security is a broader concept that focuses on protecting all types of information, including digital and physical data. Cybersecurity is a subset that specifically focuses on protecting digital systems and networks.
2. How can I protect my personal data online?
Use strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication, keep software updated, and avoid sharing sensitive information on unsecured websites.
3. What is the CIA Triad in information security?
The CIA Triad stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These are the core principles of information security to ensure data is private, accurate, and accessible when needed.
4. Are free antivirus programs enough for information security?
While free antivirus programs offer basic protection, they may not cover advanced threats. Paid solutions often provide better malware detection, firewalls, and real-time monitoring.
5. How often should I backup my data?
It depends on the volume and importance of your data. Critical data should be backed up daily, while less sensitive data can be backed up weekly or monthly.
6. What is encryption, and why is it important?
Encryption converts information into a code that only authorized users can read. It is essential for protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
7. Can small businesses afford information security measures?
Yes, even small businesses can implement cost-effective solutions like strong passwords, firewalls, employee training, and cloud backup services.
8. What should I do if my data is breached?
Immediately isolate affected systems, change passwords, notify relevant parties, and investigate the cause to prevent future incidents.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Use a Password Manager: Helps create and store complex passwords securely.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication: Adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
- Regular Security Audits: Periodically review systems to identify vulnerabilities.
- Secure Physical Access: Lock computers, servers, and storage devices in secure locations.
- Educate Continuously: Keep up-to-date with the latest security threats and trends.
- Cloud Security Measures: Ensure your cloud provider has strong security policies.
- Limit Data Sharing: Only share information with trusted sources and on secure platforms.
Conclusion
Information security is no longer optional in today’s digital age. Protecting data from unauthorized access, theft, or loss is critical for individuals, businesses, and organizations. By understanding the principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and implementing practical measures such as encryption, strong passwords, and employee training, you can significantly reduce the risk of security incidents.
Although challenges and risks exist, the benefits of robust information security far outweigh the disadvantages. It helps safeguard sensitive data, maintain trust, comply with regulations, and ensure smooth business operations. Remember, information security is an ongoing process that requires constant attention, monitoring, and improvement.
Whether you are securing your personal devices or managing a business network, taking proactive steps now can save you from potential losses and headaches in the future. Start small, stay consistent, and gradually implement advanced measures to ensure your data remains safe and secure. With the right approach, information security becomes a natural part of your digital life, giving you peace of mind and confidence in a connected world.