Introduction
Network Security is one of the most important topics in today’s digital world. As businesses, schools, and individuals rely more on the internet, protecting data has become a top priority. From online banking to cloud storage, every digital action depends on secure networks. Without proper protection, sensitive information can be stolen, damaged, or misused.
Network Security focuses on protecting computer networks from unauthorized access, attacks, and data loss. It includes tools, rules, and practices designed to keep networks safe. Even small organizations and home users face cyber threats every day. Hackers no longer target only large companies. Anyone connected to the internet can be at risk.
For beginners, Network Security may sound complex. However, the basic ideas are simple and practical. You do not need to be a technical expert to understand how network protection works. With the right guidance, anyone can learn the fundamentals and apply them effectively.
This article explains Network Security in clear and simple language. It is designed for beginners and intermediate readers who want practical knowledge. You will learn what Network Security is, why it matters, how to implement it step by step, and what mistakes to avoid. By the end, you will have a solid understanding of how to keep networks safe in real-life situations.
What is Network Security?
Network Security is the process of protecting a computer network from unauthorized access, misuse, and cyber threats. It involves both hardware and software solutions that work together to secure data and systems.
At its core, Network Security controls who can access a network and what they can do once inside. It also protects data while it is being transmitted across the network. This ensures that sensitive information stays private and unchanged.
Network Security includes several layers of protection. Each layer addresses different types of threats. For example, firewalls block unwanted traffic, while antivirus software detects harmful programs.
In simple terms, Network Security acts like a security guard for digital systems. It checks every entry point, monitors activity, and stops suspicious behavior before damage occurs. Without it, networks become easy targets for attackers.
Why is Network Security Important?
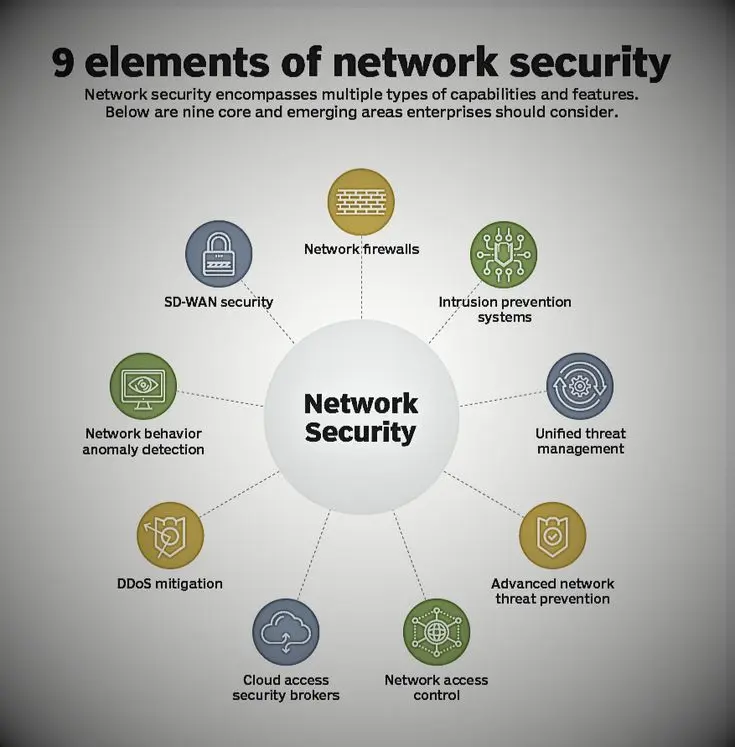
Network Security is important because cyber threats are increasing every year. Attackers use advanced methods to steal data, disrupt services, and cause financial loss.
One major reason Network Security matters is data protection. Personal details, financial records, and business information must remain confidential. A single breach can expose thousands of records.
Another reason is business continuity. Network attacks can shut down systems for hours or days. This can stop operations and damage customer trust.
Network Security also helps meet legal and regulatory requirements. Many industries require strong security measures to protect user data. Failure to comply can result in heavy fines.
Most importantly, Network Security builds trust. Customers and users feel safer when they know their data is protected. This trust is essential for long-term success in the digital world.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Understand Your Network
Start by identifying all devices connected to your network. This includes computers, servers, routers, and mobile devices. Knowing what you need to protect is the first step.
Create a simple network map. This helps you see how data flows and where risks may exist. Clear visibility improves security planning.
Step 2: Set Strong Access Controls
Limit access to authorized users only. Use strong passwords and change them regularly. Avoid sharing login details.
Implement role-based access. Users should only access what they need for their work. This reduces the risk of misuse.
Step 3: Install Firewalls
Firewalls act as barriers between trusted and untrusted networks. They monitor incoming and outgoing traffic.
Use both hardware and software firewalls if possible. This adds an extra layer of protection against threats.
Step 4: Use Antivirus and Anti-Malware Tools
Install reliable antivirus software on all devices. Keep it updated to detect new threats.
Run regular scans to identify and remove malicious programs before they cause harm.
Step 5: Encrypt Network Data
Encryption protects data during transmission. Even if attackers intercept it, they cannot read it.
Use secure protocols for communication. Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information.
Step 6: Monitor Network Activity
Regular monitoring helps detect unusual behavior early. Look for unexpected traffic or login attempts.
Use logs and alerts to stay informed. Quick action can prevent serious damage.
Step 7: Update Systems Regularly
Keep operating systems and software up to date. Updates often fix security weaknesses.
Ignoring updates leaves networks exposed to known threats.
Step 8: Educate Users
Train users about safe online behavior. Teach them how to recognize suspicious emails and links.
Human awareness is a key part of Network Security.
Benefits of Network Security
- Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access
- Reduces the risk of cyber attacks
- Ensures smooth and reliable network operations
- Builds trust with users and customers
- Helps meet legal and compliance requirements
- Prevents financial losses caused by breaches
Disadvantages / Risks
- Implementation can be costly for small organizations
- Requires ongoing maintenance and updates
- Complex systems may need skilled professionals
- Overly strict rules can reduce user convenience
- Poor configuration can create security gaps
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many people rely only on basic security tools. This is not enough in today’s threat environment.
Another mistake is using weak passwords. Simple passwords are easy to guess and compromise security.
Ignoring software updates is also common. Outdated systems are prime targets for attackers.
Some organizations forget user training. Even the best tools cannot protect against careless behavior.
Finally, failing to monitor network activity can delay threat detection and increase damage.
FAQs
What is the main goal of Network Security?
The main goal of Network Security is to protect data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access and cyber threats. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
Is Network Security only for large companies?
No, Network Security is important for everyone. Small businesses and individuals are also targets for cyber attacks. Basic security measures are essential for all users.
How often should security systems be updated?
Security systems should be updated regularly. Automatic updates are recommended to ensure protection against the latest threats.
Can Network Security prevent all attacks?
No system is completely secure. However, strong Network Security greatly reduces risks and limits damage from attacks.
What skills are needed to manage Network Security?
Basic knowledge of networking, security tools, and user management is helpful. Advanced systems may require professional expertise.
Why is user education important?
Users are often the weakest link. Training helps them avoid risky actions and supports overall security efforts.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
Always use layered security. Multiple protection levels are more effective than a single solution.
Perform regular security audits. This helps identify weaknesses before attackers do.
Back up data frequently. Backups reduce the impact of ransomware and data loss.
Use network segmentation. Separating network areas limits the spread of threats.
Finally, stay informed about new security trends. Continuous learning improves long-term protection.
Conclusion
Network Security is no longer optional in the modern digital environment. Every connected system faces potential threats, and ignoring security can lead to serious consequences. From data theft to service disruption, the risks are real and growing.
The good news is that Network Security does not have to be complicated. By understanding basic concepts and following simple steps, anyone can improve their network protection. Strong access controls, regular updates, monitoring, and user education form a solid foundation.
For beginners and intermediate users, focusing on practical actions makes a big difference. Start small, improve gradually, and stay consistent. Security is an ongoing process, not a one-time task.
As technology continues to evolve, so will cyber threats. Staying prepared and proactive is the best defense. With the right approach, Network Security can protect your data, support growth, and build trust in an increasingly connected world.




